Design Proposal
According to the EPA, Americans spend on average, 93% of their time indoors and only 7 % outdoors. Typically, indoor environments house concentrations of pollutants that are often two to five times higher than the typical outdoor environment. Since we spend half of our time indoors, our indoor environment's level of comfort should be prioritized. This can be achieved by emphasizing the interactivity between the building envelope, the conditions of the outdoor environment, and the occupants. During the design phase, thermal implications are always an important factor however moisture is still consistently neglected. In reality, both conditions play an essential role in building design and energy efficiency. This can be addressed by utilizing porous materials that operate as moisture buffers. In this study, the abilities of these materials will be compared to one another as well as the moisture buffering capacity of soil. The soil will represent the presence of a green wall because green walls are a technology that is typically employed to regulate interior humidity levels. This additional part of the study will expose how passive design can be more effective and efficient than active design.
Research Question : Which material (wood, clay brick & concrete brick) has the highest absorption capacity?
Materials with high moisture absorption capacity can be used to passively control moisture conditions without the need to employ sustainable building technologies such as green walls.
Research Question : Which material (wood, clay brick & concrete brick) has the highest absorption capacity?
Materials with high moisture absorption capacity can be used to passively control moisture conditions without the need to employ sustainable building technologies such as green walls.
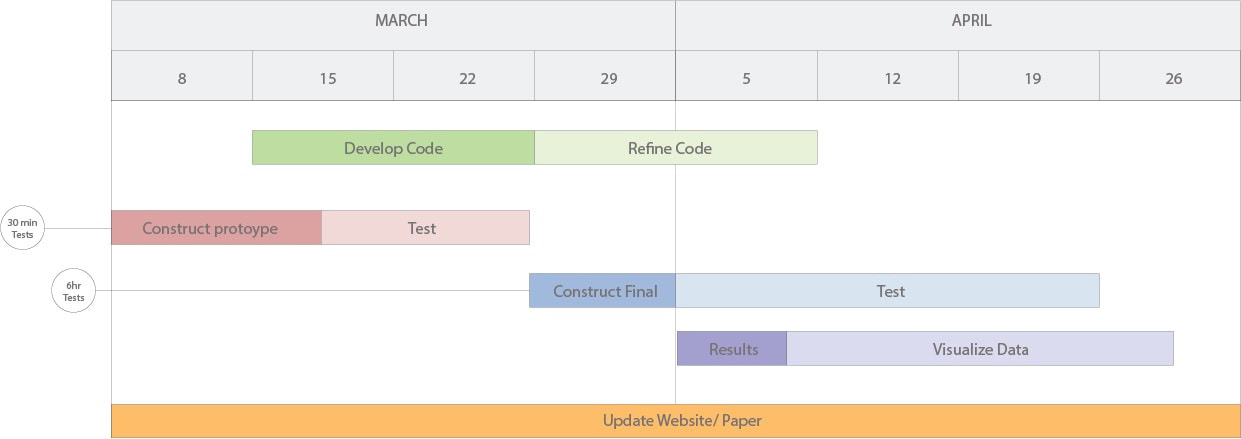
ITERATIONS AND MOCKUPS
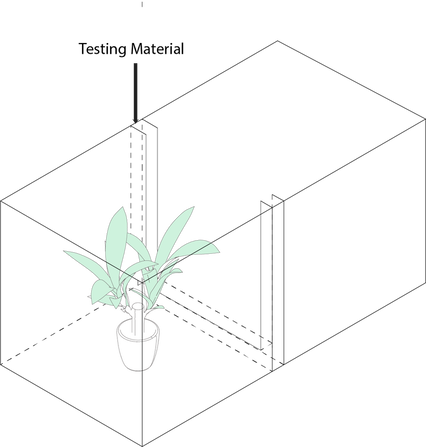
First Iteration (6x6 acrylic)
Lessoned learned: Instead of moisture passing through the material and testing two compartments, make one compartment and place testing materials in there.
Lessoned learned: Instead of moisture passing through the material and testing two compartments, make one compartment and place testing materials in there.
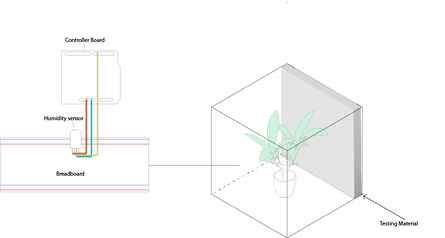
Second Iteration and electronic control strategy (6x6 Acrylic)
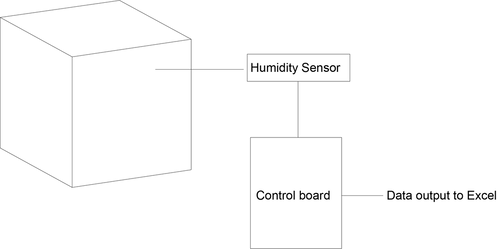
Lesson Learned: No need for plant and breadboard. Humidity sensor can be directly inputted into the control board.
Lesson Learned: No need for plant and breadboard. Humidity sensor can be directly inputted into the control board.
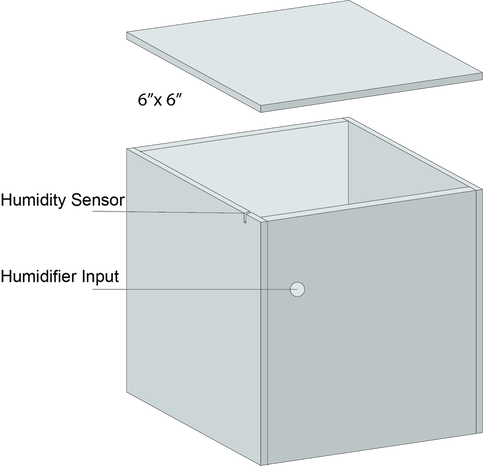
Final Mockup (6x6 Foam box - 1/16" thick material)
Lesson Learned: Thicker material should be used to allow sturdiness, Design needs to be airtight. Duct tape is used to seal box.
Lesson Learned: Thicker material should be used to allow sturdiness, Design needs to be airtight. Duct tape is used to seal box.