Design Proposal
 Figure 1: Traditional Laos Home
Figure 1: Traditional Laos Home
Background:
Studies the idea of evaporative cooling, in the realm of humidity and food storage. Uncovers the ideas behind storing food for longer by decreasing the overall temperature in which its stored. It breaks down the idea behind how temperature affects food soiling and the possibility of slowing that process by using different materials which absorbed different amounts of water in tandem with evaporative cooling to store food. Food storage varies from region to region in the region of Laos food is stored under the home with a hot humid and exposed to the outside environment. In order to solve the issue of food spoilage in Laos we could create a centralized unit used to store food in a zero energy way. This study can be used to better understand the basics of food spoilage I had to dig into the literature on how food spoils and the ways to slow that process, more in-depth in my literature review, Food spoils when bacteria are able to eat away at the food. In order to slow that process, the removal of that bacteria is possible but also the use of slowing the growth of the bacteria which is a more effective method due to the abundance of bacteria. To slow the growth of bacteria we tend to use fridges which is a tool that cools the temperature of the environment and it slows the growth of bacteria. So if we can replicate the cooling effect in a low-tech environment we could preserve food for longer.
Studies the idea of evaporative cooling, in the realm of humidity and food storage. Uncovers the ideas behind storing food for longer by decreasing the overall temperature in which its stored. It breaks down the idea behind how temperature affects food soiling and the possibility of slowing that process by using different materials which absorbed different amounts of water in tandem with evaporative cooling to store food. Food storage varies from region to region in the region of Laos food is stored under the home with a hot humid and exposed to the outside environment. In order to solve the issue of food spoilage in Laos we could create a centralized unit used to store food in a zero energy way. This study can be used to better understand the basics of food spoilage I had to dig into the literature on how food spoils and the ways to slow that process, more in-depth in my literature review, Food spoils when bacteria are able to eat away at the food. In order to slow that process, the removal of that bacteria is possible but also the use of slowing the growth of the bacteria which is a more effective method due to the abundance of bacteria. To slow the growth of bacteria we tend to use fridges which is a tool that cools the temperature of the environment and it slows the growth of bacteria. So if we can replicate the cooling effect in a low-tech environment we could preserve food for longer.
Research question:
How can we harness the energy of passive evaporative cooling in tandem within different materials to create a cooled temperature, and which materials will create a colder temperature?
Hypothesis:
Less permeable materials such as loose sand will create a cooler temperature using passive evaporative cooling versus more permeable materials such as gravel which will create a less cool temperature.
|
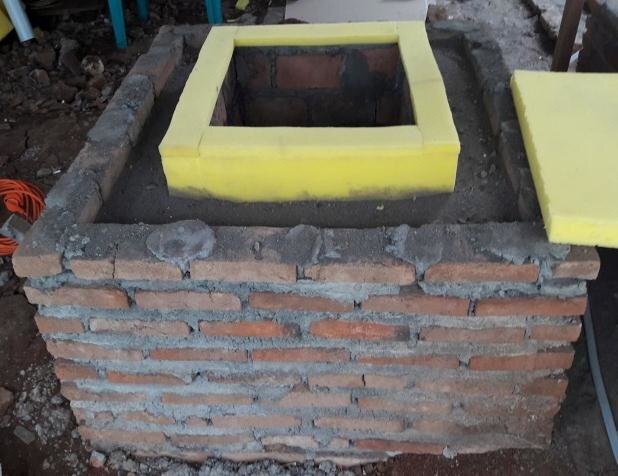
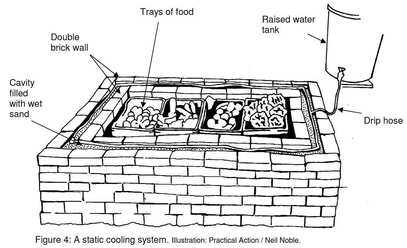
Figure 2: ZECC (Zero Energy Cooling Chamber) Diagram
https://srrweb.cc.lehigh.edu/app/ZECC#:~:text=The%20Zero%20Energy%20Cool%20Chamber,efficiency%20than%20your%20typical%20fridge. |
Figure 3: ZECC (Zero Energy Cooling Chamber)
|
Mockup
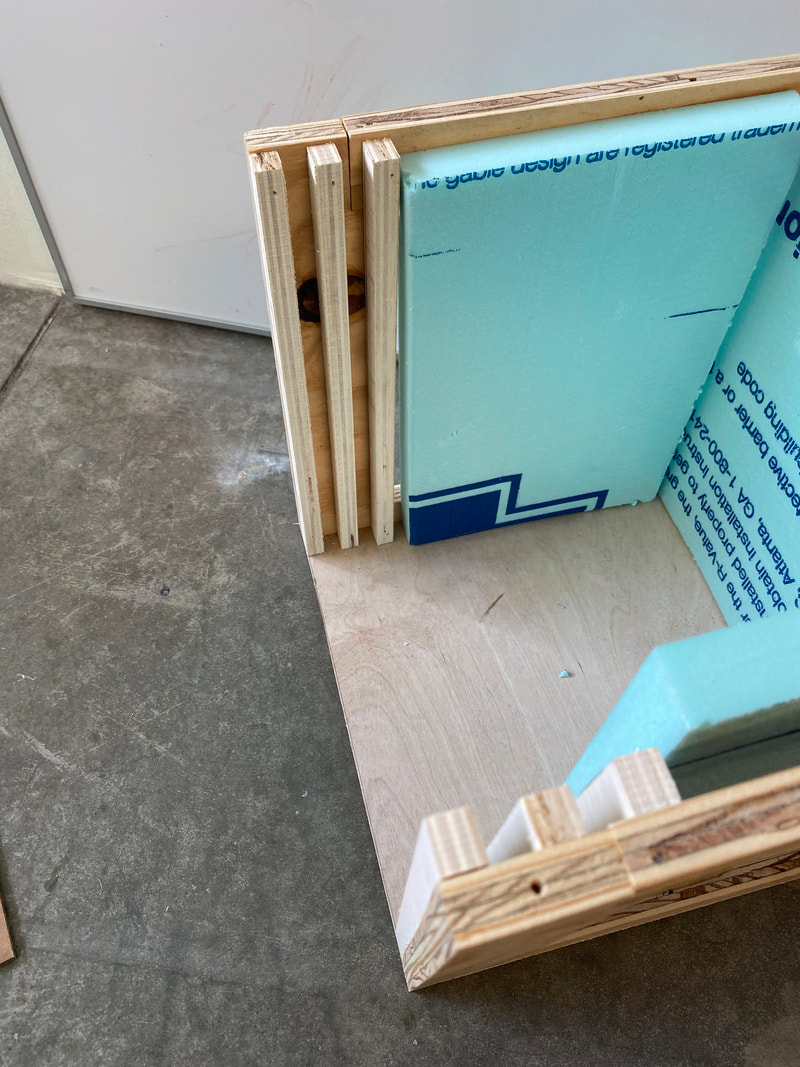
Test Chamber -Version One
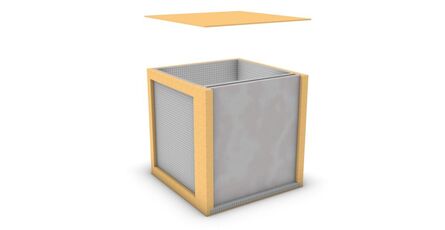
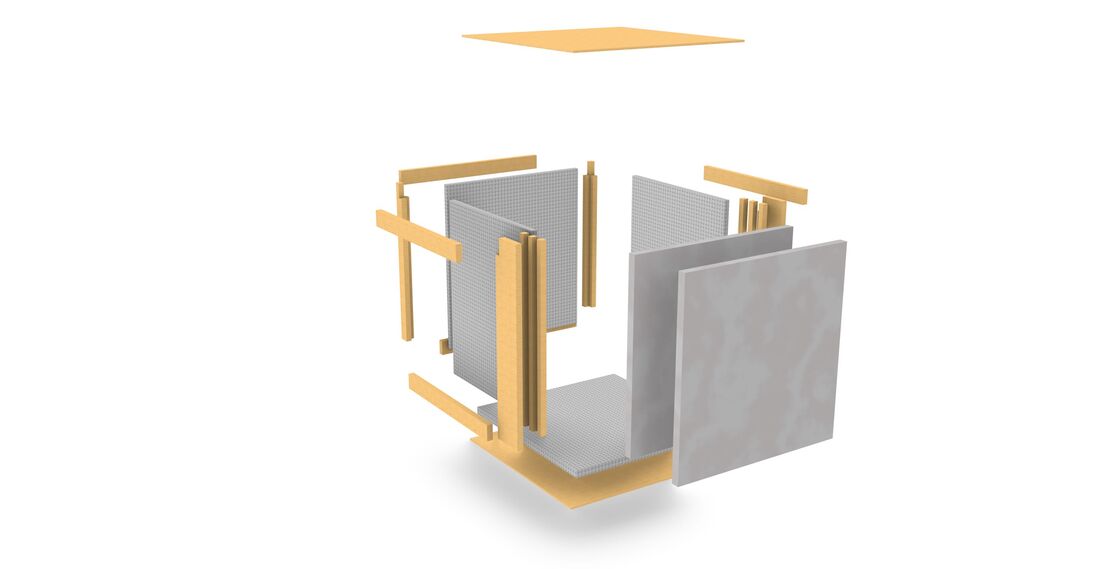
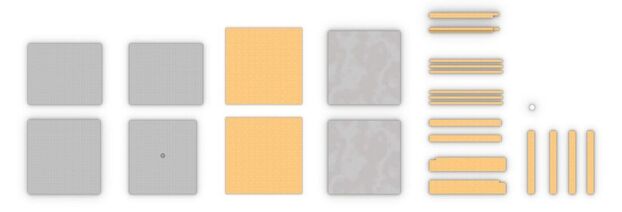
Figure 4: Schematics for version one of my Proposal mockup
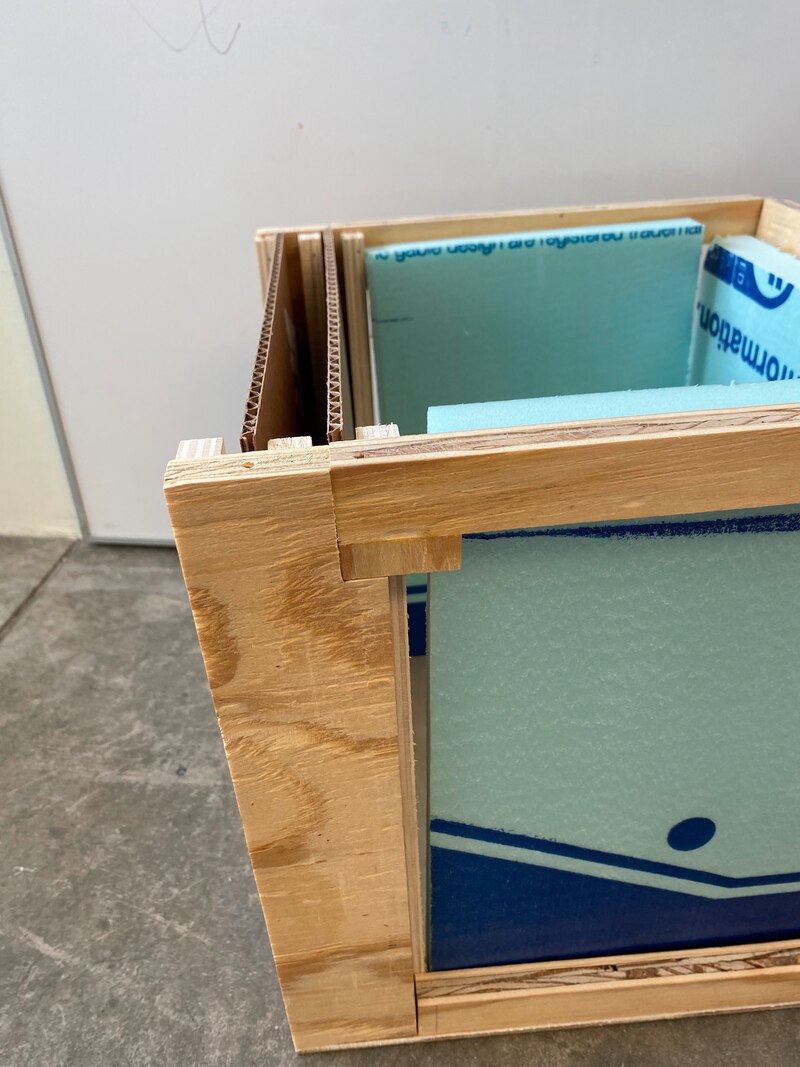
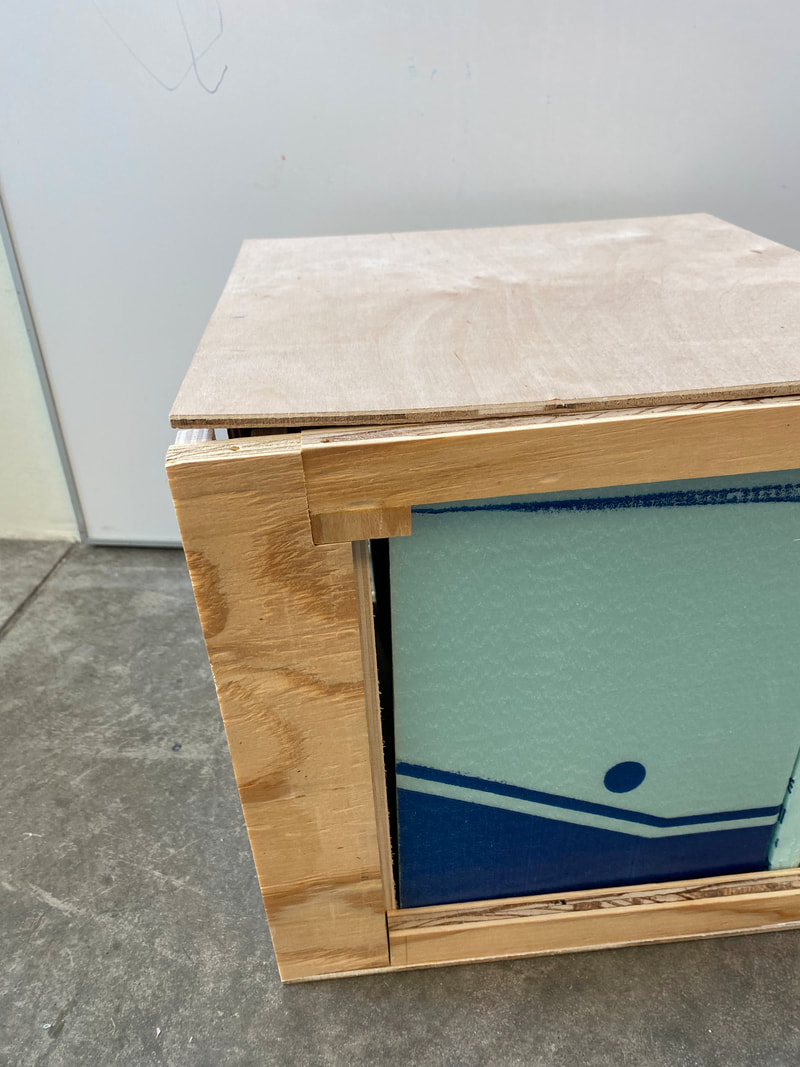
Mock-up Product
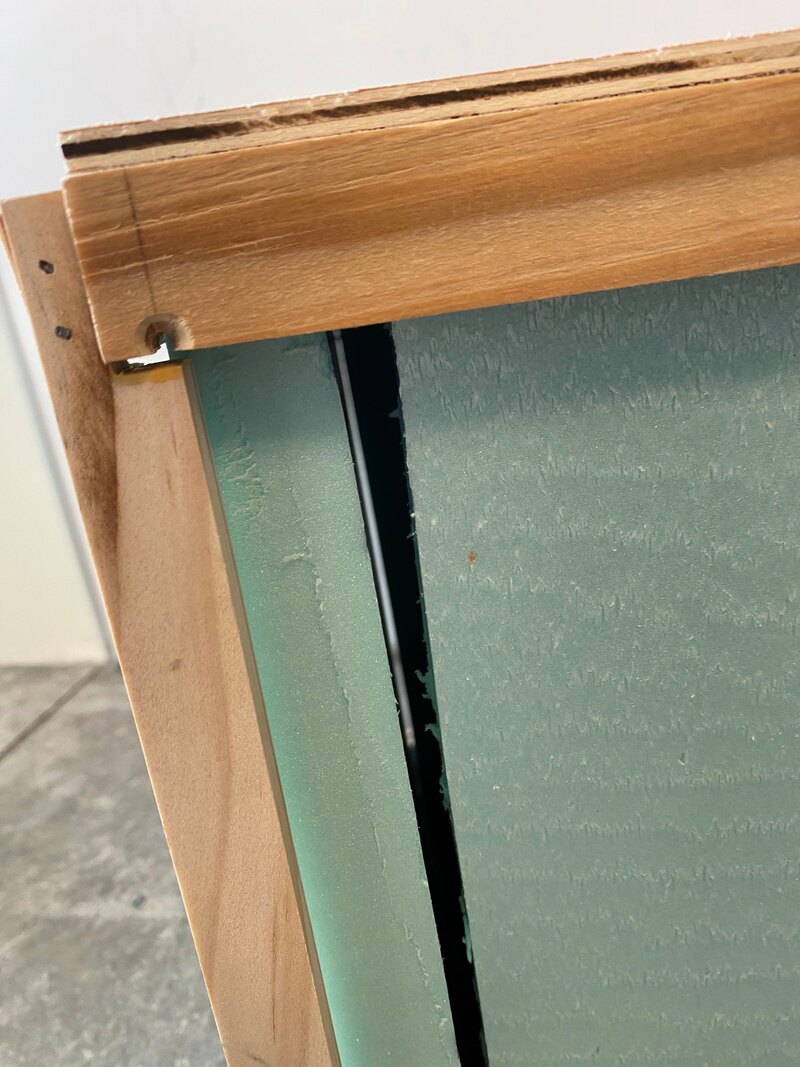
Mock Up Errors
Figure 5: Mock up construction & testing errors; to be reconciled in final prototype
Schedule for Testing:
Test & Development Stages: |
Date: |
Develop Mockup |
February 22nd |
Create Prototype |
March 1st - March 8th |
Construct Prototype |
March 8th - March 22nd |
Develop Electronics |
March 15th - March 22nd |
Present Prototype |
March 22nd |
Update Website |
March 22th - March 29th |
Perform Tests |
March 29th - April 12th |
Revise |
April 12th - April 19th |
Organize Findings & Data |
April 19th - May 3rd |
Present Findings/Next Steps? |
May 10th |
Proposal |
Background |
Construction |
Methodology |
Results |