-
Projects
- Environment Box
- Passive Refrigeration
- Water Cooling
- Fog Catching
- Roof Geometries
- Optimal Insulation
- Cooler Windcatcher
- Green Machine
- Mitigating Humidity
- Convective Air Flow
- Styrene Reuse
- Thermal Reflection
- ETFE Rigidification
- Phase Change Materials
- Polar Reflection
- Cavity Depth Variation
- Vapor Permeability
- Algae Facade
- Moisture Buffering
- Engineered Geometries
- Recycled Desiccant Materials
- Living Wall
- Solar Shading Facades
- SHADESin.reACTION
- Low-Fab Dehumidification
- Breathing Wall
- Urban Heat Island
- Acoustical Design
- Latent Heat of PCM's
- Insulative Qualities of Air
- About
- Lectures
- Assignments
- Workshops
- Syllabus
- Resources
Proposal: Measure the latent heat of PCM
Water is used as experimental material
Two steps
1. Measuring the amount of electricity required to heat the ice-water mixture to 100℃.
2. Using the formula to calculate the energy consumed.
Question
1. How to find changes in temperature in a container?
2. Which tool can be used to heat water?
3. How to measure the amount of electricity consumed?
4.How to calculate the latent heat of water by electricity consumption?
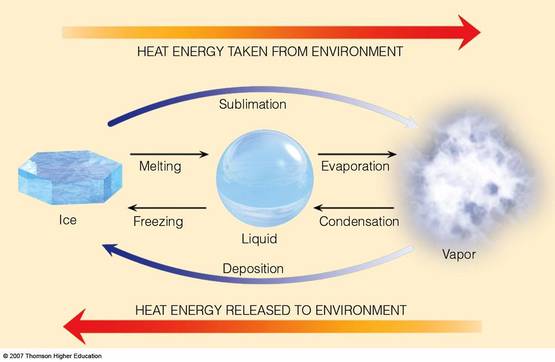
A PCM is a substance with a high latent heat (also called the heat of fusion if the phase change is from solid to liquid) which is capable of storing and releasing large amounts of energy at a certain temperature. A PCM stores heat in the form of latent heat of fusion which is about 100 times more than the sensible heat. For example, latent heat of fusion of water is about 334kJ/kg whereas sensible heat at 25° Celsius (77°F) is about 4.18kJ/kg. PCM will then release thermal energy at a freezing point during solidification process (Figure Phase Change of a PCM). Two widely used PCMs by many of us are water and wax. Think how water requires significant amount of energy when it changes from solid phase to liquid phase at 0°C (32°F) or how wax extends the burning time of a candle. Moreover, the cycle of the melting and solidification can be repeated many times.
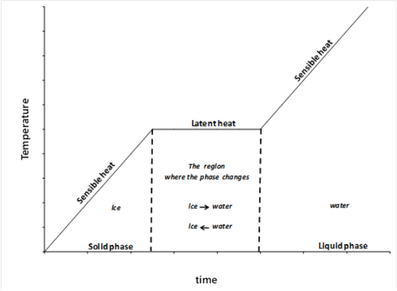
Thermal storage based on sensible heat works on the temperature rise on absorbing energy or heat, as shown in the solid and liquid phases in the picture. When the stored heat is released, the temperature falls, providing two points of different temperature that define the storage and release functions. Phase change materials are conceptually different, however. They operate by storing energy at a constant temperature while phase change occurs, for example from solid to a liquid, as illustrated in the center of the picture. As heat is added to the material, the temperature does not rise; instead heat drives the change to a higher energy phase. The liquid, for example, has kinetic energy of the motion of atoms that is not present in the solid, so its energy is higher. The higher energy of the liquid compared to the solid is the latent heat. When the solid is fully transformed to liquid, added energy reverts to going into sensible heat and raising the temperature of the liquid.
Sources:
Said Al-Hallaj & Riza Kizilel
Said Al-Hallaj & Riza Kizilel